When Good Writers Cross Bad Lines

This screenshot shows the homepage of Verified Market Research, a firm that gives you the lowdown on market trends. Their site highlights their expertise across various industries and really emphasizes data-driven insights. This is helpful context for understanding things like the increasing need for tools that help writers paraphrase effectively and ethically.
We've all stared at a brilliant article, itching to use its insights, but terrified of plagiarism. Truthfully, many writers caught plagiarizing aren't trying to be dishonest. They just blur the lines between inspiration and imitation. I’ve chatted with tons of editors and professors, and they agree. They've seen it firsthand – well-meaning writers accidentally straying into plagiarism territory.
One huge misunderstanding? Thinking that swapping a few words counts as paraphrasing. Switching "big" for "large" or shuffling the sentence structure isn't nearly enough if the original phrasing is largely the same. I call this the “synonym shuffle,” and it's a trap. Real paraphrasing means understanding the core idea. Close your source material, then explain it like you're teaching it to someone. This shows true comprehension and avoids plagiarism.
The internet, with its readily-available information, makes accidental plagiarism even easier. It’s tempting to copy and paste, thinking a quick edit is sufficient. But this often creates “patchwork paraphrasing” – bits of original text mixed with slightly tweaked phrases. Still plagiarism! Effective paraphrasing requires a mental shift: focus on understanding, not just rewording. This also helps when using paraphrasing tools, so you don't have to lean on questionable AI-generated content.
The demand for original content is clear in the growth of the plagiarism detection software market. It was valued at $468.19 million in 2023 and is projected to hit $1,126.90 million by 2031. That’s huge! It reflects the need for tools that help create authentic work. Want to see more? Check out the plagiarism detection software market here. It’s a fascinating glimpse into how originality is shaping the digital world. This heightened awareness just underscores how crucial it is to master paraphrasing without plagiarizing.
The Mental Shift That Changes Everything
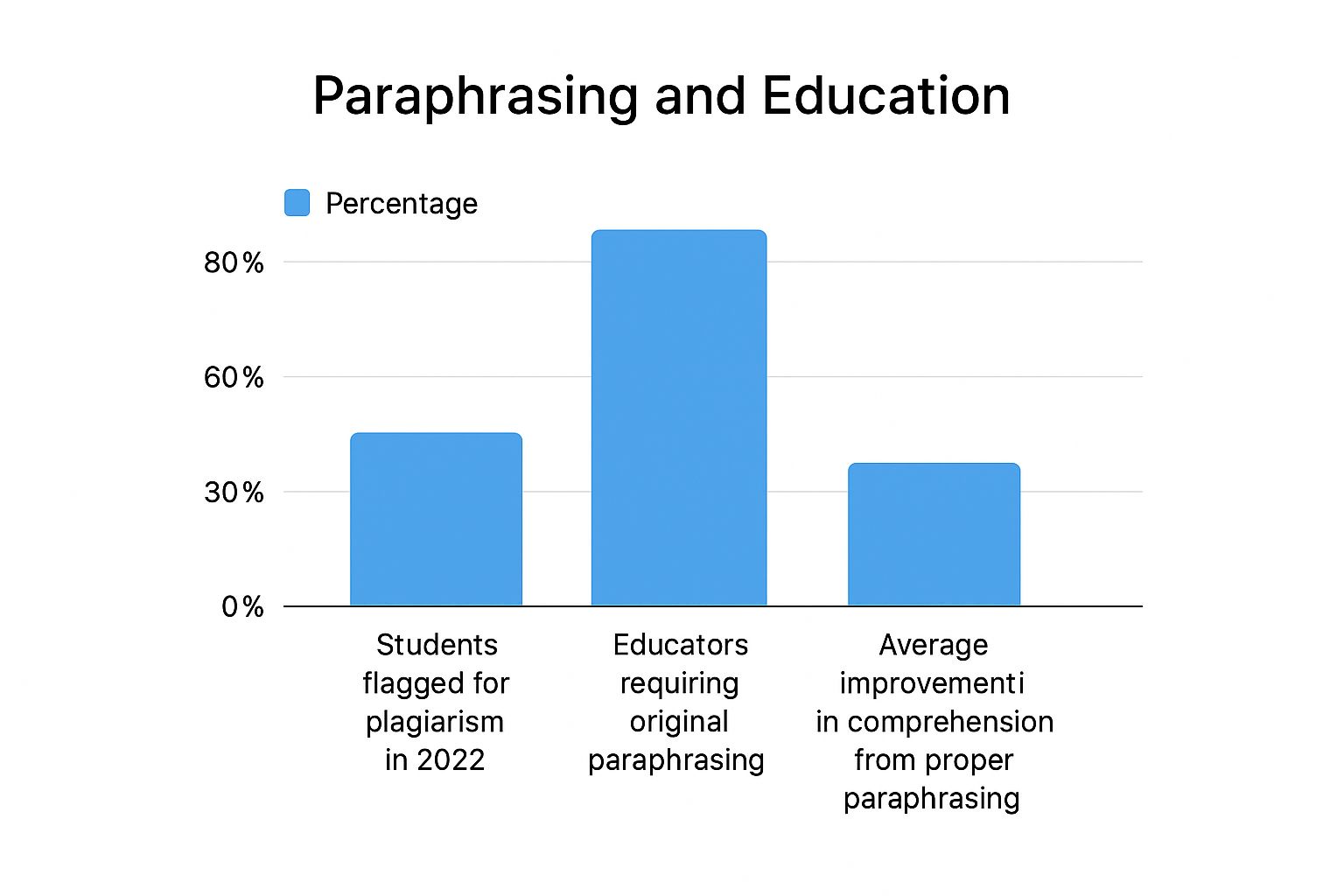
This infographic highlights some interesting data about plagiarism and paraphrasing. It shows that a surprisingly large number of students struggle with plagiarism, while educators place a huge emphasis on original paraphrasing. Interestingly, the data also reveals a strong connection between paraphrasing well and actually understanding the material better. This underscores the importance of not just rewriting to avoid plagiarism, but really getting the information.
That mental shift—from rewriting to understanding—is the real secret to paraphrasing without plagiarizing. Think of it this way: you can't explain something to someone else unless you understand it yourself, right? The people who are best at paraphrasing aren't just good at swapping words around; they're good at grasping the core ideas.
The "Close the Book" Method
Here’s a trick I use all the time, which I call the "close the book" method. After reading something you need to paraphrase, close the book (or article, or whatever). Then, explain the concept out loud, as if you’re talking to a friend. This forces you to use your own words and rely on your own understanding, not the original text. Plus, it helps your own voice and style come through naturally.
Of course, sometimes certain ideas are just harder to paraphrase than others. This is especially true with technical or specialized language. It's tempting to just plug in synonyms, but that often misses the mark. This is where a solid understanding of the material becomes even more important. Even experienced writers can be tempted to cut corners, and a writing accountability app can be surprisingly helpful for staying focused and avoiding accidental plagiarism.
This leads us to another key point: recognizing when you've truly grasped an idea versus when you're still relying too heavily on the original source. This self-awareness is the difference between amateur and pro-level paraphrasing. It lets you keep the original meaning intact while making the content your own. By focusing on this mental shift, you’re building a solid foundation for effective, plagiarism-free writing.
Here's a table summarizing some common paraphrasing techniques:
Effective Paraphrasing Techniques Comparison
A comprehensive comparison of different paraphrasing methods, their effectiveness, difficulty level, and best use cases
| Technique | Effectiveness | Difficulty Level | Best For | Time Required |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Summarizing | High | Medium | Condensing information | Moderate |
| Using synonyms | Medium | Low | Simple phrases | Low |
| Changing sentence structure | High | High | Complex sentences | High |
| "Close the Book" method | High | Medium | Ensuring comprehension | Moderate |
| Combining techniques | Highest | High | Most situations | High |
This table shows that while using synonyms might seem easy, it’s often not the most effective technique. Combining different techniques, especially with the "Close the Book" method, tends to yield the best results, although it does require more effort and time. The key takeaway? True understanding is the foundation of great paraphrasing.
Tools That Actually Help (And Ones That Don't)

This image shows a bunch of digital tools writers can use. They look cool, but here's the thing: not every tool is good for paraphrasing without plagiarizing. Some are lifesavers, others… not so much.
Let's be honest, there are tons of paraphrasing tools out there. Some are fantastic, others…well, you get the idea. From my experience, some are great for suggesting synonyms, which is helpful when you’re searching for the perfect word. But relying only on these tools can make your writing sound stiff and unnatural. Plus, some tools spit out content that’s way too close to the original, which misses the whole point of paraphrasing.
AI Assistants: Friend or Foe?
AI writing tools can be super helpful, but they shouldn't do all the work for you. I like to use them for brainstorming, exploring different angles on an idea. For example, I might give an AI a really complicated paragraph and see how it simplifies it. This can give me fresh ideas for explaining the same concept in my own words. It's crucial, though, to double-check the AI's work. Make sure it’s accurate and hasn’t accidentally created any factual errors or plagiarism. You might find this interesting: Paraphrase Content.
Traditional techniques, like the "close the book" method we talked about earlier, are still super effective. Really understanding the material is the best way to avoid plagiarism. This is better than even the most expensive software for creating truly original content. It helps you absorb the information and express it in your own voice. This focus on originality is driving the demand for anti-plagiarism software. The market is expected to grow by $4.92 billion between 2024 and 2028, with a CAGR of 30.42%. This growth shows how important paraphrasing without plagiarism is becoming, especially in education. Learn more about this trend: Discover more insights into the anti-plagiarism market.
Workflow Strategies for Success
Good writers often use a mix of tools and techniques. They might use a Thesaurus for finding better words, an AI assistant for brainstorming, and then their own understanding to write the final paraphrase. This combined approach uses the strengths of different tools while keeping you in control. Good note-taking and organizing your sources are also key. I use digital note-taking apps along with good old pen and paper to keep track of my sources and avoid accidental plagiarism. In the end, the best tools are the ones that fit your writing process and help you create original, high-quality work.
Navigating The Wild West Of Digital Sources

This image really hits home how much digital content we swim through every day. Remember the days when it was all about books and journals? Now, it's a constant stream of online info, from social media to AI-generated text. That shift makes paraphrasing a whole new ballgame.
Paraphrasing used to be so much simpler. Citing a textbook was a breeze. But how do you cite a deleted tweet or a TikTok video that's all about visuals and sound? Traditional guidelines just don't cut it when you're dealing with Instagram stories, YouTube comments, and AI-generated content.
Let's say you're writing a blog post about the latest social media trends. You find a brilliant point on an influencer's Instagram story, but it's gone in 24 hours. How do you even cite that? This is where good documentation becomes essential. Screenshots and archived links are your best friends. It's the way we have to work with fleeting content now. And then there are the ethical questions around paraphrasing AI-generated content. We're still figuring out how to handle originality and authorship in that space. If you’re interested in AI and writing, here’s an article about AI Writing Assistant.
Paraphrasing Multimedia: A New Frontier
Visual content adds another layer of complexity to paraphrasing. Think about capturing the essence of a meme, an infographic, or a short video clip in writing. You're not just restating words, you're interpreting meaning and describing key elements. It’s about getting the core message across in a different format. But even with these new challenges, the core principle remains the same: deeply understanding the source material. This means really engaging with the content, no matter the format. This focus on deeper understanding is reflected in the anti-plagiarism software market. It was valued at $737 million in 2021 and is projected to reach $4,806 million by 2030, with a CAGR of 23.3%. The increasing use of digital tools is driving this growth, highlighting the importance of original content. For more on this, check out this resource on the anti-plagiarism market.
These new challenges force us to rethink our approach. We need practical ways to make smart decisions in situations where the old rules are blurry. This means developing a solid understanding of intellectual property, considering ethical implications, and always focusing on accurate attribution. This is how we navigate the constantly changing world of digital content creation while staying credible and maintaining academic integrity.
Citations That Feel Natural, Not Forced
This screenshot, from the Purdue OWL's guide on APA style, shows examples of basic in-text citations. It illustrates how to attribute ideas, both with and without directly using the author's name in the sentence. This highlights how important clear and consistent citations are, regardless of how you introduce the source.
Perfect paraphrasing is pointless if your citations are sloppy. You want your sources to enhance your writing, not weigh it down. Think of it like this: the best writing seamlessly integrates its sources, making them feel like a natural part of the conversation.
The Art of the Signal Phrase
One of my favorite techniques for smooth citations is using signal phrases. These little phrases act like bridges, guiding your reader from your thoughts to the source and back again. Instead of just plopping in a citation, you can say something like, "According to Smith (2023),…" or "Research by Jones (2022) suggests…".
These phrases not only provide a nice transition, but they also add context. You can even get more creative with phrases like, "Smith (2023) challenges this idea…" or "Jones (2022) builds upon this argument by…". It adds a layer of depth and shows you’re really engaging with the material. If you're feeling stuck, a citation generator can be a helpful resource.
Another crucial aspect is knowing when to quote directly and when to paraphrase. Direct quotes pack a punch, especially when the original wording is powerful or unique. Paraphrasing, on the other hand, is great for explaining complex ideas in your own words and keeping your writing style consistent. The key is finding the right balance.
Handling Multiple Sources and Citation Anxiety
I'll be honest, even I still get citation anxiety sometimes. Am I over-citing? Under-citing? The trick is to remember the why behind citations. We cite to give credit and to make it easy for readers to find our sources. A good rule of thumb: cite anything that isn't common knowledge or that you pulled directly from another source.
Citing multiple sources in one paragraph can feel tricky. Just be sure to clearly connect each idea to the right source. Varying your signal phrases can help, and sometimes listing multiple sources in one citation is totally fine, especially if they support the same point. You'll get a feel for it over time.
Let's take a look at some common citation scenarios to make things even clearer. The table below breaks down some real-world challenges writers face and how to handle them effectively.
| Scenario | Citation Required? | Best Practice | Common Mistake | Example |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Summarizing multiple sources for background information | Yes | Briefly cite each source within the summary. | Not citing sources at all, or only citing one. | "Research suggests a link between sleep and memory (Walker, 2017; Stickgold, 2005)." |
| Paraphrasing an idea from a single source | Yes | Cite the source at the end of the paraphrased sentence. | Not citing the source, thinking paraphrasing avoids citation. | "The brain consolidates memories during sleep (Walker, 2017)." |
| Directly quoting a phrase | Yes | Use quotation marks and cite the source, including the page number. | Not using quotation marks or not including the page number. | "Sleep is the 'ultimate performance enhancer'" (Walker, 2017, p. 52). |
| Presenting common knowledge | No | No citation needed. | Citing a source for widely known facts. | "The earth revolves around the sun." |
| Building upon an idea from a source with your own analysis | Yes | Cite the original source and then expand on it. | Not citing the original source. | "Walker (2017) argues that sleep is crucial for memory. This may explain why…" |
This table highlights the different situations you might run into when citing sources, and the proper way to handle each. Remember, clarity and accuracy are key. With a bit of practice, citations will become second nature!
The Mistakes Everyone Makes (And How To Avoid Them)
Let's be honest, some paraphrasing slip-ups are so incredibly common they're almost predictable. The "synonym shuffle" is a classic. You know the one – swapping out words in the original text for synonyms, thinking you've magically crafted something new. Been there, done that, bought the t-shirt. It simply doesn't work. It's like rearranging deck chairs on the Titanic; the core structure is identical, and plagiarism checkers will catch it every time.
Another frequent trap is clinging too tightly to the original sentence structure. Even with different vocabulary, mirroring the initial phrasing too closely is still plagiarism. Think of it as tracing a drawing. Different colors, same outline—still not your original creation. You have to restructure, rephrase, and genuinely own the idea.
Paraphrasing vs. Summarizing: Two Different Beasts
Many people confuse paraphrasing with summarizing. Both involve using your own words, but their aims differ. Paraphrasing means restating a particular passage or idea with similar length, whereas summarizing condenses a larger piece of information into a shorter, more concise form. This distinction is critical for dodging unintentional plagiarism. Summarizing when you should be paraphrasing usually means omitting key details and remaining too close to the source.
The Psychology of Paraphrasing Pitfalls
Sometimes, the biggest paraphrasing hurdles aren't technical; they're mental. We're all susceptible. Ever felt too comfortable with a topic and figured you could paraphrase from memory? That overconfidence can easily lead to accidental plagiarism. Or what about that deadline pressure that makes you rush through paraphrasing, taking shortcuts, and hoping for the best? Yeah, I've been there too. It's never pretty. For a polished, plagiarism-free piece, a grammar checker can be a lifesaver. It helps make sure your rewritten content is clear, concise, and error-free.
Practical Self-Checks for Success
So, how do you avoid these traps? One effective strategy is to read the original, set it aside, and then explain the concept to someone else (or even just to yourself!). This forces you to internalize the information, the foundation of effective paraphrasing. Another excellent tip? Compare your paraphrase to the original, side-by-side. Look for any lingering similarities in phrasing or structure. Anything questionable? Keep refining. Honest self-assessment is the key. It’s about developing that inner editor that knows when your paraphrase is truly original.
Your Personal Paraphrasing System
So, we've talked a lot about paraphrasing the right way. Now, let's get personal. How do you build a system that fits your writing style? This isn't about generic tips; it's about building a system that actually works for you.
Know Your Strengths and Weaknesses
Let’s be honest. Everyone has writing quirks. Do you swap synonyms constantly? Maybe you get tripped up by complex sentences. Figuring out your weaknesses is the first step towards improving. Perhaps you're a big-picture thinker who gets bogged down in details. Maybe technical stuff is easy, but you struggle with nuanced arguments. Knowing your tendencies helps you target those areas where you can get better.
Building Your Quality Control Checklist
Once you know your weak points, build a checklist. Mine includes things like: "Did I actually close the source material before I started writing?" and "Does this sound like me?" Yours will probably be different. The important thing is to make it specific to how you write. This checklist becomes your safety net, catching those little mistakes before they become big problems.
Real-World Writing: Deadlines and Difficult Sources
Let’s face it, deadlines happen. We don't always have hours to meticulously craft every sentence. That’s where your personalized system becomes a lifesaver. Having a go-to process helps you create good work, even when you're pressed for time. It’s your fallback when you're short on time, but need to make sure your writing is still original.
For example, if I'm up against a tight deadline, I'll use my "close the book" method and focus on explaining the core ideas simply and clearly. My checklist helps me double-check that I haven't accidentally plagiarized anything or missed key information.
Keep Learning and Growing
Paraphrasing is a skill you hone over time. Review your work. Look for places you can tighten up your phrasing, add more of your own voice, or explain things more clearly. Even small improvements add up. By constantly learning and tweaking your methods, you'll become a more confident and skilled writer.
Ready to level up your writing? SmartStudi offers a set of tools to help you create original, plagiarism-free content. From AI detection and paraphrasing help to grammar checks and citation generation, SmartStudi helps you write with confidence and integrity. Check out all the features and benefits.
