Understanding What Separates Good Paraphrasing From Plagiarism

Paraphrasing is a vital skill for any student wanting to avoid plagiarism. However, the difference between acceptable paraphrasing and plagiarism can be confusing. This is where a solid understanding of the basic principles is important. Changing a few words or restructuring a sentence isn't enough for proper paraphrasing. The key is understanding the difference between simply rephrasing and truly reinterpreting the original text.
More Than Just Swapping Synonyms
Effective paraphrasing requires a complete restructuring of the original thought, expressed in your own words. This means more than just finding synonyms. It involves deeply understanding the source material so you can accurately represent its meaning without directly copying its language. For instance, take the sentence: "The cat sat on the mat." A weak paraphrase would be: "The feline sat upon the rug." Although different words are used, the sentence structure and meaning are much too similar.
Transforming the Original Idea
A stronger approach involves altering both sentence structure and voice, all while keeping the original meaning. A good paraphrase could be: "On the mat rested a cat." This version communicates the same information using different wording and structure. This demonstrates a genuine grasp of the concept and a fresh presentation. This method allows you to seamlessly incorporate information into your writing without over-relying on direct quotations.
The Importance of Citation
Even with accurate paraphrasing, citing your source is critical. Failing to do so, even when paraphrasing, is considered plagiarism. Paraphrasing to avoid plagiarism is an ongoing challenge in academics. A 2010 Texas Tech study showed that 68 percent of faculty members reported seeing students copy or paraphrase without proper citation. For more statistics, visit: Learn more about plagiarism prevention and awareness. Properly crediting your sources demonstrates academic integrity and helps readers find the original material. Ultimately, mastering correct paraphrasing ensures your work is both original and credible.
Mastering The Art Of Transformation: Core Paraphrasing Strategies
Ready to move beyond simply swapping synonyms? This section dives into the core strategies that elevate paraphrasing from a plagiarism avoidance tactic to a powerful writing technique. We'll explore how to genuinely transform source material while preserving its core message, creating truly original content that strengthens your own work.
Structural Reorganization: Reshaping the Flow
One of the most effective paraphrasing strategies involves restructuring the original text. This goes beyond simply rearranging sentences; it's about fundamentally altering how the information flows. For example, if a source presents information chronologically, consider organizing it thematically in your paraphrase. This encourages deeper engagement with the material and allows you to present it in a way that best supports your argument. This method also helps avoid patchwriting, where small sections of the original are merely rearranged.
Strategic Synonym Use: Choosing the Right Words
While synonym substitution alone isn't enough for effective paraphrasing, choosing the right synonyms is crucial. This involves understanding the nuances of language and selecting words that accurately reflect the original meaning while incorporating your own voice. For instance, instead of always replacing "important" with "significant," consider alternatives like "crucial," "essential," or "vital," depending on the context. You might be interested in: How to master paraphrasing and other writing skills.
Voice Changes: Shifting the Perspective
Another powerful technique is shifting the voice of the original text. This might involve changing from active to passive voice, or vice-versa. You can also adjust the tone and style to better suit your writing. For example, if the source uses a formal, academic style, you could paraphrase it using a more conversational tone, if appropriate for your audience. This transformation demonstrates a deeper understanding of the source and allows for smoother integration into your own work.
Conceptual Reframing: Looking Through a Different Lens
The most advanced paraphrasing strategy involves conceptual reframing. This means examining the information from a new angle and presenting it in a fresh light. This approach requires a strong grasp of the subject matter and the ability to synthesize information. Think of it as explaining a complex concept simply – you need to rephrase without losing the core meaning. This method avoids plagiarism and demonstrates intellectual engagement with the material. Through these combined strategies, you can ensure your paraphrased content is both original and impactful.
Navigating AI Tools and Automated Paraphrasing: What Works and What Doesn't

AI paraphrasing tools offer a convenient way for students to quickly reword content. However, using these tools effectively and ethically requires careful consideration. This section explores the benefits and risks of AI paraphrasing, helping you understand responsible usage and plagiarism avoidance.
The Allure of Automated Assistance
AI paraphrasing tools can be valuable for deciphering complex texts. By simplifying language, these tools clarify difficult concepts. They also offer alternative phrasing, expanding vocabulary and refining writing style. This makes them useful for brainstorming and exploring different ways to express your ideas.
The Pitfalls of Automated Paraphrasing
Relying solely on AI paraphrasing tools to avoid plagiarism is risky. Many tools simply substitute synonyms, leading to awkward phrasing and distorted meanings. This can make writing sound unnatural and may result in unintentional plagiarism if the sentence structure remains too similar to the original source. This can create bigger problems than the ones you're trying to solve.
Furthermore, some AI-generated content is easily flagged by plagiarism detection software like Turnitin. These tools often produce predictable text that lacks originality. Many students are now working on methods to refine and "humanize" output from tools like ChatGPT to ensure it aligns with their personal voice and style, thereby avoiding plagiarism. For tips on refining ChatGPT output, check out how to humanize text from ChatGPT. There's a growing trend of using automated tools to modify text and circumvent plagiarism detection. AI paraphrasing tools, for example, can rephrase text while maintaining the original meaning, creating seemingly original and coherent content. However, statistics show that despite these advances, in 2017, 38% of students admitted to paraphrasing or copying sentences from written sources without proper attribution. Find more detailed statistics here.
Using AI Tools Ethically
The key to ethical use of AI paraphrasing tools is to treat them as writing aids, not substitutes for comprehension. Use them to explore different phrasing and clarify difficult passages, but always review and edit the output carefully. Ensure the rewritten text accurately reflects the original meaning and integrates seamlessly with your writing style. Remember: true paraphrasing involves transforming knowledge and ideas, not just words. By actively engaging with the material and using AI tools responsibly, you can leverage technology to improve your writing while maintaining academic integrity.
Getting Citations Right: The Make-Or-Break Factor In Paraphrasing
Even perfectly paraphrased content can be flagged as plagiarism if not cited correctly. This section offers a guide to mastering citations, focusing on APA, MLA, and Chicago styles, and clarifying when and how to cite paraphrased material.
Why Citations Matter, Even With Paraphrasing
Paraphrasing involves expressing someone else's ideas in your own words. However, the original idea still belongs to the original author. Citations acknowledge this intellectual ownership and allow readers to trace the source of the information.
This builds credibility and avoids accusations of plagiarism. Proper attribution is essential for academic integrity.
Common Knowledge vs. Citable Information
Understanding the difference between common knowledge and information requiring citation is crucial. Common knowledge refers to widely known facts readily available in multiple sources. For example, "Paris is the capital of France" doesn't need a citation.
However, specific interpretations, analyses, or data from a particular source do require attribution. This ensures accuracy and intellectual honesty. Failing to cite specific information can lead to plagiarism.
To illustrate the importance of careful review and proper citation even when using paraphrasing tools, consider the infographic below:
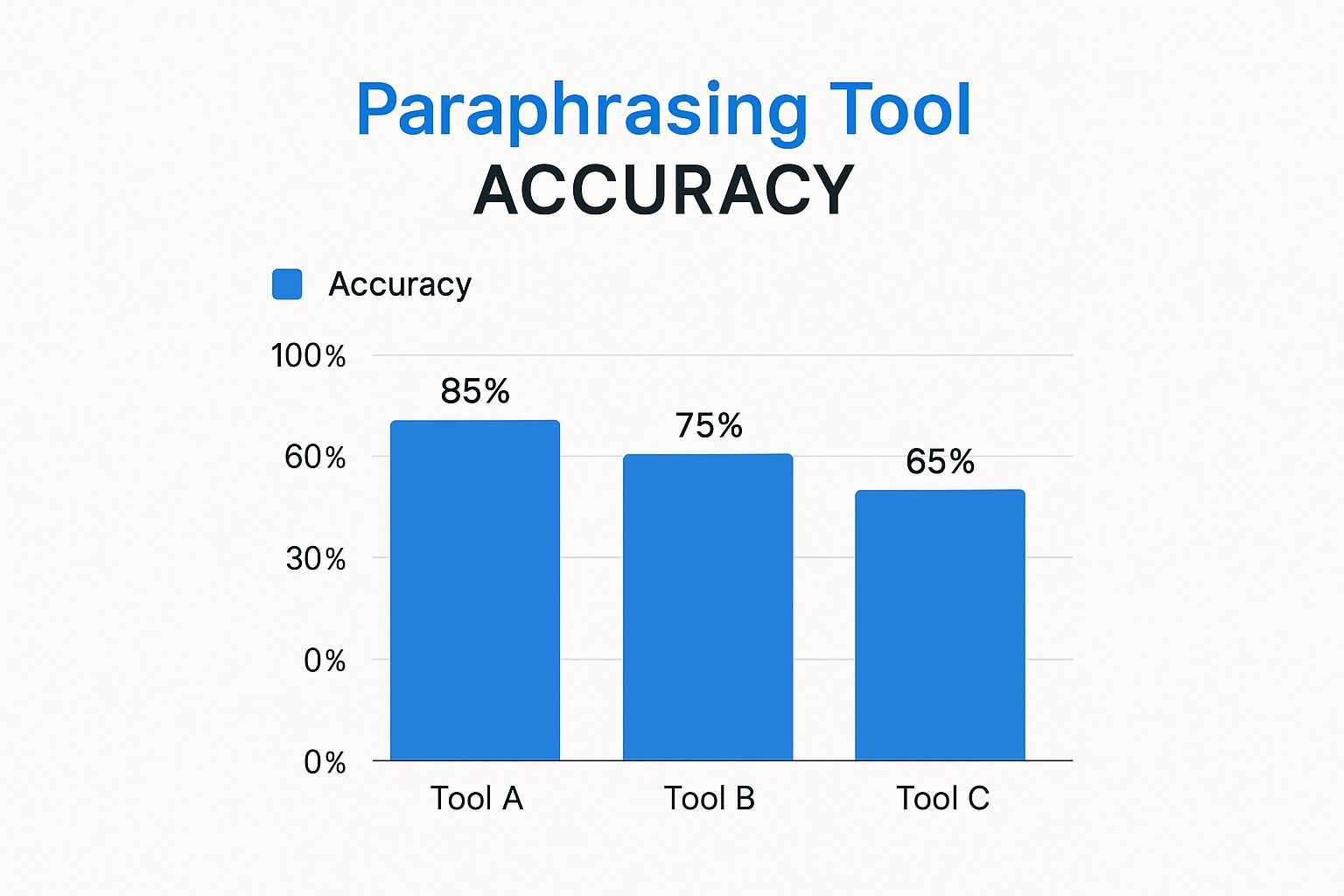
As shown, Tool A boasts the highest accuracy at 85%, significantly outperforming Tool C, which scores only 65%. This underscores the need to select reliable tools and critically evaluate their output. Many students are exploring ways to refine and personalize the output from tools like ChatGPT to ensure it aligns with their own voice and style, and to avoid plagiarism. For helpful tips on refining this process, you might consider reading about how to humanize text from ChatGPT.
To further clarify when citations are necessary, let's examine a few examples:
To help illustrate the different citation requirements, the following table provides examples and reasoning for various content types:
Citation Requirements for Different Types of Paraphrased Content
A comparison showing when citations are required for different categories of paraphrased information.
| Content Type | Citation Required | Example | Reasoning |
|---|---|---|---|
| Common Knowledge | No | The Earth revolves around the Sun. | This is a widely known fact. |
| Specific Statistic | Yes | According to a 2023 study by Smith et al., 75% of students prefer online learning. | This is specific data from a particular source. |
| Interpretation of Data | Yes | Jones (2022) argues that the decline in reading comprehension is linked to increased screen time. | This is an interpretation specific to the author. |
| General Idea from a Specific Source | Yes | As Brown (2021) suggests, effective communication is essential for team success. | While the idea might be general, attributing it to a specific source gives it context and authority. |
The table above demonstrates the nuances of citation requirements. While general knowledge doesn't need a citation, specific data, interpretations, and even general ideas derived from a specific source require proper attribution.
Mastering Different Citation Styles
Different academic disciplines use different citation styles. APA, MLA, and Chicago are among the most common. Each style has specific formatting guidelines for in-text citations and bibliographies.
Learning these nuances prevents citation errors and strengthens your academic writing. Resources like citation generators can be helpful tools.
Integrating Citations Seamlessly
Citations should enhance your writing, not disrupt it. Integrate them smoothly by introducing the author or source before presenting the paraphrased information. Use signal phrases like "According to…" or "As noted by…" to connect the citation to the paraphrased content.
This creates a clear link between your writing and the source material. Well-integrated citations make your writing more persuasive and credible.
By understanding these core principles and practicing proper citation techniques, you can ensure that your paraphrased content is both informative and academically sound. This strengthens your arguments, builds credibility, and demonstrates respect for intellectual property. Accurate citations are a hallmark of strong academic work.
Avoiding The Traps: Common Paraphrasing Mistakes That Sink Students
Effective paraphrasing goes beyond simply substituting synonyms. It involves a true understanding of the source material and the ability to reshape it while preserving accuracy. Unfortunately, many students, even those with the best intentions, stumble into common traps that can inadvertently lead to plagiarism. Let's explore some of these pitfalls and how to steer clear of them.
The Perils of Patchwriting
Patchwriting, one of the most frequent mistakes, involves stitching together phrases and sentences from the original source with minimal changes. This might include swapping a few words or slightly altering the sentence structure, but the essence of the original text remains easily identifiable. For instance, changing "The quick brown fox jumps over the lazy dog" to "The fast brown fox leaped over the sleeping dog" constitutes patchwriting, not paraphrasing.
Insufficient Source Transformation
Another common error is not sufficiently altering the source material. Even if you refrain from directly copying, over-reliance on the original sentence structure and vocabulary can still be classified as plagiarism. This is particularly true for technical terminology or specialized concepts. You must demonstrate a grasp of the information by expressing it in your own words. Ensure your approach aligns with academic integrity by following established code review best practices.
Citation Confusion
Even with flawless paraphrasing, omitting a citation is plagiarism. Citing your source is vital. It credits the original author's ideas and guides readers to the primary source. Remember, citation is non-negotiable, even when paraphrasing. Inconsistent or absent citations damage your credibility and can result in academic penalties.
The Trouble With Technical Terminology
Paraphrasing technical terminology, proper names, or specialized concepts presents a unique challenge. While you should retain these specific terms, rephrasing the surrounding text can demonstrate understanding. For example, instead of "Photosynthesis is the process used by plants to convert light energy into chemical energy," you might say, "Plants utilize photosynthesis to transform light into chemical energy."
Misquoting or Misrepresenting Information
Accuracy is paramount when paraphrasing. Ensure your paraphrase faithfully reflects the original author's intent. Accidentally misrepresenting or twisting the meaning can lead to inaccurate and misleading information, compromising your work's integrity and potentially misinforming your audience. Explore advanced techniques in our guide on How to master undetectable paraphrasing using AI.
Recognizing Your Weak Spots
Understanding these common paraphrasing pitfalls and actively working to avoid them will strengthen your paraphrasing skills. This will allow you to produce original, well-supported academic work. Learning to identify these errors in your own writing is essential for avoiding plagiarism and achieving academic success. Practice and careful review are key to mastering this important skill.
The Global Reality: Why Paraphrasing Skills Matter More Than Ever

Understanding the global impact of plagiarism underscores the importance of paraphrasing for academic success. This goes beyond simply avoiding penalties. It's about preparing for a professional world where ethical information use is paramount. This section explores the widespread nature of plagiarism and how strong paraphrasing skills can significantly benefit your academic and professional future.
Plagiarism: A Growing Global Concern
Globally, plagiarism is a growing concern. Statistics reveal its prevalence across diverse educational settings. In the U.S., 3.2% of students were caught plagiarizing in 2021. Furthermore, in 2017, 25% of graduate students admitted to paraphrasing or copying content without proper citation. Learn more about plagiarism statistics. These figures highlight the ongoing challenges students face with attribution and the need for effective paraphrasing techniques.
To better understand the scope of this issue, let's examine some data across different academic levels and regions. The following table provides a snapshot of plagiarism rates and common types.
Plagiarism Statistics by Academic Level and Region
| Academic Level | Plagiarism Rate | Region | Most Common Type |
|---|---|---|---|
| High School | 20% | North America | Copying and Pasting |
| Undergraduate | 15% | Europe | Insufficient Paraphrasing |
| Graduate | 10% | Asia | Improper Citation |
| Online Programs | 25% | Global | Contract Cheating |
Note: These figures are illustrative and may vary based on specific studies and reporting methods.
As this data suggests, plagiarism is a pervasive issue affecting all levels of education. Understanding regional variations and the most prevalent forms of plagiarism can inform targeted interventions and educational strategies.
Cultural Differences and Academic Integrity
Cultural differences in academic writing further complicate the issue of plagiarism. What's considered acceptable paraphrasing can vary significantly across different regions and educational systems. Some cultures may emphasize collaborative learning, while others prioritize individual authorship and original thought. This can create unique challenges for international students navigating these diverse expectations.
Institutional Responses and Long-Term Consequences
Academic institutions take plagiarism very seriously, often imposing severe consequences. These can range from failing grades and suspension to expulsion in the most serious cases. The impact, however, extends far beyond immediate academic penalties. A reputation for plagiarism can hinder future opportunities, including graduate school admissions, employment prospects, and overall professional credibility.
Paraphrasing for Success
Strong paraphrasing skills are a crucial investment in your future. The ability to accurately and ethically incorporate sources strengthens your arguments and builds credibility as a researcher and writer. It demonstrates a true understanding of the material. Mastering paraphrasing allows you to contribute meaningfully to academic discourse while upholding the highest standards of integrity. By developing these skills now, you are not just avoiding plagiarism; you are building a foundation for long-term success.
Building Paraphrasing Skills That Last: Your Path To Academic Confidence
Strong paraphrasing skills are essential for academic success, but they don't develop overnight. They require dedicated practice and a commitment to continuous improvement. This section offers practical strategies to refine your paraphrasing techniques, including targeted exercises, self-assessment, and utilizing available resources. You'll discover how to create personalized workflows that ensure quality and consistency, even when under pressure.
Practice Makes Perfect: Targeted Exercises for Improvement
Like any skill, paraphrasing improves with consistent practice. Targeted exercises can significantly refine your ability to rephrase information while maintaining accuracy. Consider incorporating these strategies:
-
Summarization Drills: Condense lengthy passages into concise summaries. This forces you to identify the core arguments and express them in your own words.
-
Paraphrase Comparisons: Paraphrase the same source text multiple times using different approaches. Comparing these versions will highlight your strengths and weaknesses.
-
Reverse Engineering: Analyze well-cited paraphrases in academic articles and attempt to reconstruct the original source material. This "backward" approach helps you understand the nuances of effective paraphrasing.
These exercises will help you develop a deeper understanding of how to express information in different ways while accurately representing the original author's ideas.
Self-Assessment: Becoming Your Own Paraphrasing Critic
Developing a critical eye for your own writing is crucial for improvement. Regularly assessing your work helps you identify areas that need attention and track your progress. After each paraphrasing exercise, ask yourself these key questions:
- Have I genuinely transformed the original text, or simply rearranged words?
- Does my paraphrase accurately convey the original meaning and author's intent?
- Have I integrated the paraphrased material smoothly into my own writing style?
- Is my citation accurate and complete, adhering to the required style guide?
Honest answers to these questions will reveal hidden weaknesses and inform your ongoing skill development.
Seeking Feedback: Learning From Others' Perspectives
External feedback provides valuable insights you might miss on your own. Ask peers, professors, or writing center tutors to review your paraphrased work. Be receptive to their suggestions and use the feedback to refine your techniques. Sharing your work can uncover blind spots and strengthen your paraphrasing skills.
Time Management: Maintaining Quality Under Pressure
Time constraints often lead to rushed paraphrasing, which increases the risk of unintentional plagiarism. Effective time management is essential for maintaining quality, even when deadlines are tight. Implement these strategies:
-
Allocate Sufficient Time: Dedicate specific blocks of time for research and paraphrasing, avoiding last-minute efforts.
-
Break Down Large Tasks: Divide large writing assignments into smaller, manageable sections. Paraphrase individual sources as you research, rather than all at once.
-
Prioritize Difficult Sources: Tackle complex or challenging sources early in the process, leaving simpler ones for when you might be under more time pressure.
By integrating these time management techniques into your writing process, you can ensure accurate and ethical paraphrasing, even under tight deadlines.
Utilizing Resources: Tapping Into Support Systems
Don't hesitate to utilize available resources. University writing centers offer valuable guidance on paraphrasing, citation styles (MLA, APA, Chicago, etc.), and plagiarism avoidance. Online resources and style guides can provide additional support and answer specific questions.
Building Confidence: Mastering Ethical Source Incorporation
As you hone your paraphrasing skills, your confidence in ethically using sources will grow. This allows you to focus on creating strong, original work that reflects your own voice and ideas while seamlessly integrating supporting evidence. Strong paraphrasing empowers you to engage meaningfully with research, articulate complex ideas effectively, and build a solid foundation for academic success.
Ready to elevate your paraphrasing skills? SmartStudi offers AI-powered tools designed to assist students with paraphrasing, generating accurate citations, and ensuring academic integrity. Visit SmartStudi today to unlock your academic potential.
